Deepening Digitalization
In the era of deepening digitalization, innovation arises from the combination of "advancements in digital technology" and "new challenges." Particularly, the application of digital technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain across various sectors can resolve many societal challenges and foster new markets, providing a driving force for growth.
However, such transformative innovations can clash with existing social orders, giving rise to numerous social issues. For instance, while kiosks reduce costs for small business owners, they may pose additional barriers for certain vulnerable groups. Generative AI enhances work efficiency by swiftly performing tasks like translation, summarization, and image generation, yet it raises concerns about protecting the copyright of data used for training. Recently, concerns about AI technology replacing jobs have escalated.
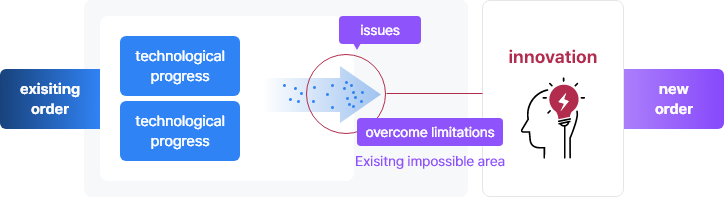
Innovation in the digital era is triggered by a combination of overcoming technological limitations and new attempts.
with the Changing Times
pIn this era of deepening digitalization, it has become increasingly challenging to adapt to changes in digital technology and address new issues using existing norms and systems. Persistent social conflicts resulting from deepening digitalization will lead to increased harm to citizens and a decline
in innovation momentum. Moreover, there is also the possibility that the proliferation of fake news using deepfake technology and the polarization caused by digital disparities could significantly undermine the universal values we have upheld thus far.
Adapting to the societal changes brought about by deepening digitalization is a matter that requires global discourse. Given the transnational application of digital technologies with their connectivity
and immediacy, forming digital norms by a single country has its limitations. Therefore, it is necessary for the international community to collaborate in addressing issues such as preparing for the risks of artificial intelligence and bridging the digital gap between nations.
Now is the time to institute a "new digital order" in response to the structural changes in our society, which we refer to as deepening digitalization. This "new digital order" represents the guiding principles for future society, encompassing laws, regulations, policy instruments, and innovative cultures (awareness, customs, etc.) essential for navigating the deepening digitalization era.
The Digital Bill of Rights will serve as the fundamental direction for establishing this global-scale
"new digital order."

-
New York
InitiativeSep. 2022“A new level of digital order is needed to protect universal human values while accepting digital changes that will penetrate into the core areas of politics, economy, society, and culture. As free citizens, we must all strive to realize the universal human values of freedom, solidarity, and human rights crossing between the real world and the digital world.”
Emphasizes the need to establish a new digital order that pursues universal human values.pursues universal human values. -
B20
SummitNov. 2022“We hope that the B20 will take the lead in establishing a digital order so that no one is left out and so that everyone can share the benefits of the digital era across borders."
Proposes participation in establishing a new digital order. -
Davos
ForumJan. 2023“The Republic of Korea will prepare the Digital Bill of Rights and contribute to the establishment of a global digital order. We will define the right to enjoy digital technology as a universal human right and present principles for resolving new issues.”
Presents the establishment of a Digital Bill of Rights that will contribute to establishing a global digital order. -
Harvard
University
SpeechApr. 2023“We must create new norms and orders in line with the new era of digital deepening. In order for the digital order to have legitimacy, currency, and sustainability, the order and norms must maximize the freedom and welfare of global citizens, ensure fair opportunities, and be especially considerate of the weak.
Emphasizes the need for a new digital order and presents fundamental principles. -
Paris
InitiativeJun. 2023“Digital is borderless, and has connectivity and immediacy. Therefore, the establishment of a universal digital order that is accepted internationally is of paramount importance. Today, I would like to talk about the digital code of ethics, which is the foundation of the digital order.”
Emphasizes the need for a new digital order and presents fundamental principles. -
UN General
Assembly Sep.2023“The Republic of Korea seeks to play a leading role in reducing the digital gap by leveraging our strengths in information and communication technology (ICT). The Republic of Korea will soon establish the Digital Bill of Rights to realize a desirable future for the digital order.”
Presents efforts to resolve the digital gap and establish the Digital Bill of Rights. -
Digital Vision
ForumSep. 2023“The Republic of Korea's Digital Bill of Rights is a charter containing the five principles by which the international community can work together to create a future digital society, and will become a standard that provides the direction for the digital deepening era.”
Presents the five fundamental principles of the Digital Bill of Rights. -
40th Cabinet
MeetingSep. 2023“The Digital Bill of Rights will contain the five principles of freedom, fairness, safety, innovation, and solidarity. I ask that each ministry establish appropriate AI and digital policies based on this Bill.”
Presents the five fundamental principles of the Digital Bill of Rights.

with the Changing Times
Digital Bill of Rights commentary, analysis and diagnosis of key issues, survey of public awareness
Ministry of Economy and Finance, Ministry of Education, Ministry of Science and ICT, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Ministry of Justice, Ministry of National Defense, Ministry of the Interior and Safety, Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism, Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs, Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Ministry of Environment, Ministry of Employment and Labor, Ministry of Gender Equality and Family, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Ministry of SMEs and Startups, Ministry of Government Legislation, Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, National Police Agency, Korean Intellectual Property Office, Korea Communications Commission, Fair Trade Commission, Financial Services Commission, Personal Information Protection Commission, Office for Government Policy Coordination.
Nov. 1, 2023-Dec.29, 2023
of the Response
to Deepening Digitalization?
The ‘Assessment of the Response to Deepening Digitalization (hereinafter referred to as ‘assessment’) is a comprehensive policy diagnosis conducted to check the status of the government
wide response to changes in digital deepening.
The main purpose of the assessment is to identify various issues and pending problems in the new era of digital deepening. More specifically, it aims to confirm the rapid changes in digital deepening,
to examine conflict situations and points of conflict with the existing order, and to identify issues and pending problems that require a prompt and timely response.
In addition, it aims to comprehensively inspect the status of each ministry's legal and institutional improvements, the progress of social discussion, and the mid- to long-term response plans for identified issues and pending problems, and as well as to analyze global trends. Through this, it
seeks to recognize the digital deepening response situation more objectively and to actively support
the necessary policy responses.
Furthermore, here are plans to conduct a regular assessment every year and to share the results
with international organizations such as the UN and the OECD, major countries such as the United
States and the United Kingdom, and developing countries, and contribute to the formation of
norms and related discussions at the global level.


of the Response
to Deepening Digitalization
The 2023 Assessment of the Response to Deepening Digitalization was conducted on a pilot basis in connection with the commentary on the Digital Bill of Rights prepared as the basic direction of the ‘new digital order’. Specifically, the promotional direction will be discussed through meetings with the relevant ministries (presided over by the Minister of Science and ICT) as a follow-up to the establishment of the Digital Bill of Rights, and at the government-wide level, twenty-six related ministries participated in the inspection of the digital deepening response status regarding fifty-two issues and pending problems in seventeen fields.
In the process of establishing the Digital Bill of Rights, the Ministry of Science and ICT identified
the main changes in digital deepening through policy research and expert consultation, and confirmed the issues and pending problems of digital deepening thus derived. In particular, through the ‘Digital Transformation Megatrend Research’ in which major domestic academic societies participated, the Ministry diagnosed changes in each area of technology, industry/economy, public/ administration,
and society/systems, and derived the expected issues and pending problems.
In addition to the derived issues and pending problems, the government has additionally
identified further digital issues and pending problems to which the relevant ministries
are responding in connection with each article of the Digital Bill of Rights. Afterwards, we identified the details of each issue and pending problem, and reviewed the policy response status and plans
of the relevant ministries in a comprehensive manner. The fifty-two issues and pending problems
of digital deepening derived through this were reclassified into seventeen areas, taking into account the relevance of each topic.
Conducted on a pilot basis as of this year, the assessment focused on identifying issues and pending problems of digital deepening that are being responded to at the pan-government level. The government intends to establish a ‘Digital New Order Establishment Plan’ (tentative name) by further specifying the detailed policy directions and mid- to long-term plans of each ministry for the
identified issues and pending problems. In addition, we plan to additionally identify new issues and pending problems through the 2024 Assessment and conduct an analysis of the global trends for each major issue.
-
4 Major Trends
- Omnidirectional expansion
of the platform - Automation-Change of work
- Virtualization-Convergence
- Hyper-personalization-Customization
4 Major Trends - Omnidirectional expansion
-
Major Changes
- Expansion of the monopoly power of
a few platforms.
Increase in irregular work. - Acceleration of automation of
high-skilled labor.
Expansion of automatio
such as generative Al. - ncreased economic and social
activities in virtual space.
Acceleration of convergence
through the use of Al. - Expansion of data-based
customized services.
Increasing use of automated
decision- making.
Major Changes - Expansion of the monopoly power of
-
Issues/Pending Problems
- Securing fairness in online platforms.
Protection of platform workers - Preparation of an education system
suitable for changes
in the digital environment.
Redesign of social security systems
and vocational education. - Establishment of norms related
to the virtual convergence economy.
Establishment of Al utilization
standards and principles for each field. - Personal information protection and
privacy security.
Establishment of norms
to ensure Al ethics and safety.
Issues/Pending Problems - Securing fairness in online platforms.

